Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes in the sinuses, the air-filled cavities in the facial skull, which can be recognized by various symptoms.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Sinusitis can cause a variety of symptoms that vary depending on its severity (acute or chronic) and the sinus affected. The most important and common symptoms are:
- Nasal congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose
- Severe or persistent runny nose, often with yellowish-green, thick or purulent nasal discharge
- Headaches and facial pain (e.g., in the forehead, cheeks, around the eyes, in the upper jaw)
- Pressure and/or pain that worsens when bending over or leaning forward
- Swelling of the face, especially over the affected sinuses
- Sensitivity to touch in the affected areas
- Impaired sense of smell (hyposmia) or complete loss of smell
- Cough, especially at night when mucus runs into the throat
- General feeling of illness, fatigue, weakness, aching limbs
- Fever (in acute sinusitis, rare in chronic sinusitis)
- Sore throat or a sticky feeling in the throat due to discharge
- Toothache (especially in the upper jaw, with sinusitis)
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Sneezing and other cold symptoms
- Pressure in the ears
- Signs of complications (rare but serious): severe swelling around the eyes, redness of the skin on the face, blurred vision, sensitivity to light, stiff neck, and very high fever
Classification of symptoms
In chronic sinusitis, the symptoms are usually less severe but persist for a longer period of time (several weeks to months). The symptoms may be localized depending on the sinus affected:
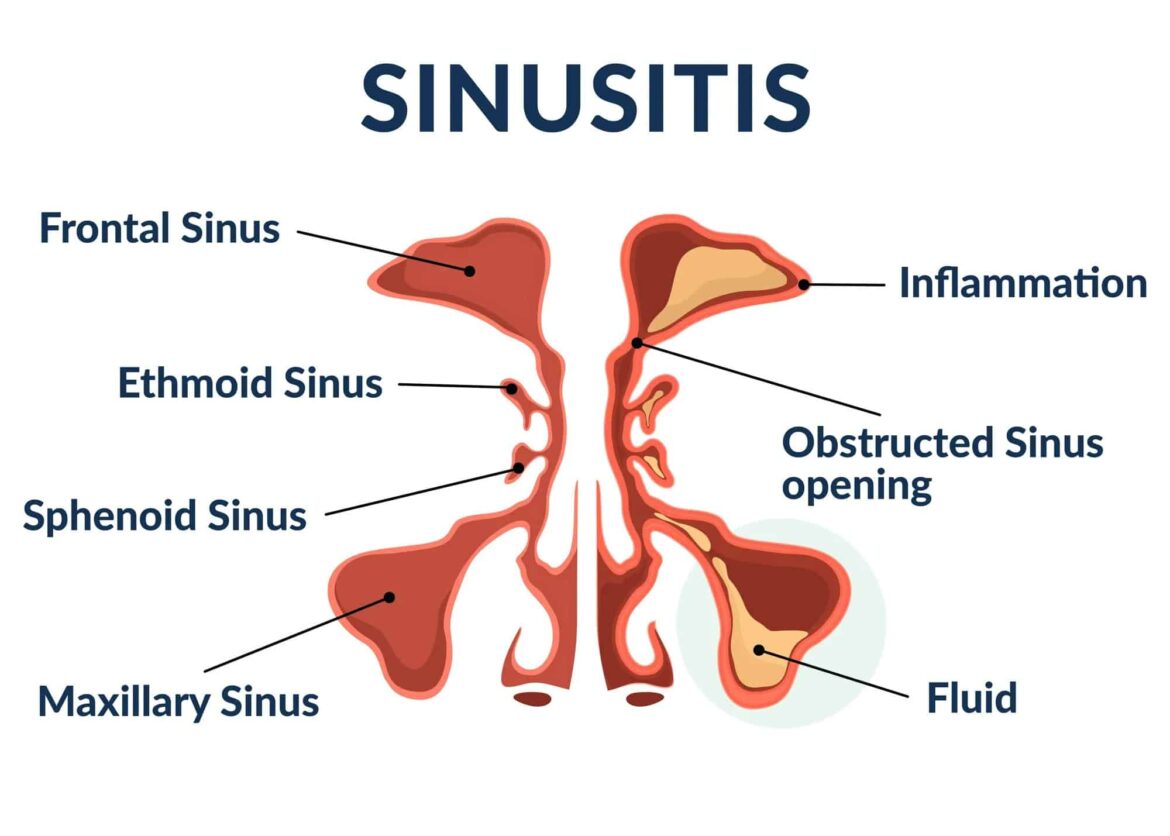
- Maxillary sinus: Pain in the upper jaw, toothache, cheek area
- Frontal sinus: Headache in the forehead
- Ethmoid cells: Pain between/behind the eyes
- Sphenoid sinus: Pain in the back of the head or diffuse pain in the head
- Important: If signs of complications occur (severe swelling, visual disturbances, neck stiffness, very high fever), seek medical attention immediately.
Treatment of sinusitis by a doctor
If you suffer from sinusitis, your doctor will usually follow these treatment steps:
- Decongestant nasal sprays or drops: These reduce swelling in the mucous membranes and allow secretions to drain more easily. However, you should not use these products for longer than a week to avoid the mucous membranes becoming dependent on them.
- Mucolytic and secretion-promoting medications: Herbal preparations such as myrtol or other secretolytics are often recommended to thin the mucus.
- Antibiotics: Your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic for bacterial, purulent inflammation.
- Pain-relieving medications: Painkillers may be used for severe pain.
- Mechanical measures: In severe cases, the doctor may insert a cotton swab soaked in decongestant drops into the nasal passage for a few minutes or, in rare cases, puncture and flush the sinuses.
- Cortisone preparations: In cases of chronic sinusitis, a cortisone-containing nasal spray can help to reduce the inflammation.
- Surgical procedures: In chronic or complicated cases, such as polyps or anatomical narrowings, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Home remedies to support treatment
You can supplement medical treatment with tried and tested home remedies. If your symptoms persist for longer than 10 to 14 days, worsen, or if you develop a fever or severe pain, please consult a doctor.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Two to three liters of water or unsweetened tea per day help to thin the mucus.
- Steam inhalation: Inhale hot steam, adding salt, chamomile, thyme, or essential oils (e.g., eucalyptus, mint, tea tree) if desired. This loosens mucus and moisturizes the mucous membranes.
- Nasal rinses: Rinse your nose with an isotonic saline solution (0.9%). This clears the nose and promotes the drainage of secretions.
- Heat applications: Red light lamps, warm compresses (e.g., flaxseed compresses) or warm, moist wraps on the forehead and cheeks are considered beneficial.
- Chicken soup and herbal teas: Chicken soup can have a mucolytic effect. Teas made from anti-inflammatory herbs such as sage, chamomile, thyme, ginger, or elderflower support the immune system.
- Elevate your head while sleeping: This allows secretions to drain better.