1.2K
Discover how to enable MSI Secure Boot and optimize your system’s security features. This article provides a detailed overview of the benefits and challenges of this technology, as well as step-by-step instructions for setup.
Definition: What is MSI Secure Boot?
Secure Boot is a security feature supported by most modern computers. It prevents untrusted software from running during the startup process, reducing the risk of malware attacks.
- Secure Boot is a feature built into UEFI firmware that ensures only trusted software is executed when the system starts up.
- When Secure Boot is enabled, a cryptographic key is used to verify the integrity of the loaded software.
- MSI Secure Boot provides additional protection against bootkits and rootkits that attempt to hide in the boot process.
- It is particularly important for systems used in sensitive environments, such as in companies or when processing personal data.
Instructions: How to enable MSI Secure Boot
Enabling MSI Secure Boot requires a few steps within your computer’s BIOS or UEFI menu. It is important that you follow these steps carefully to ensure the security of your system.
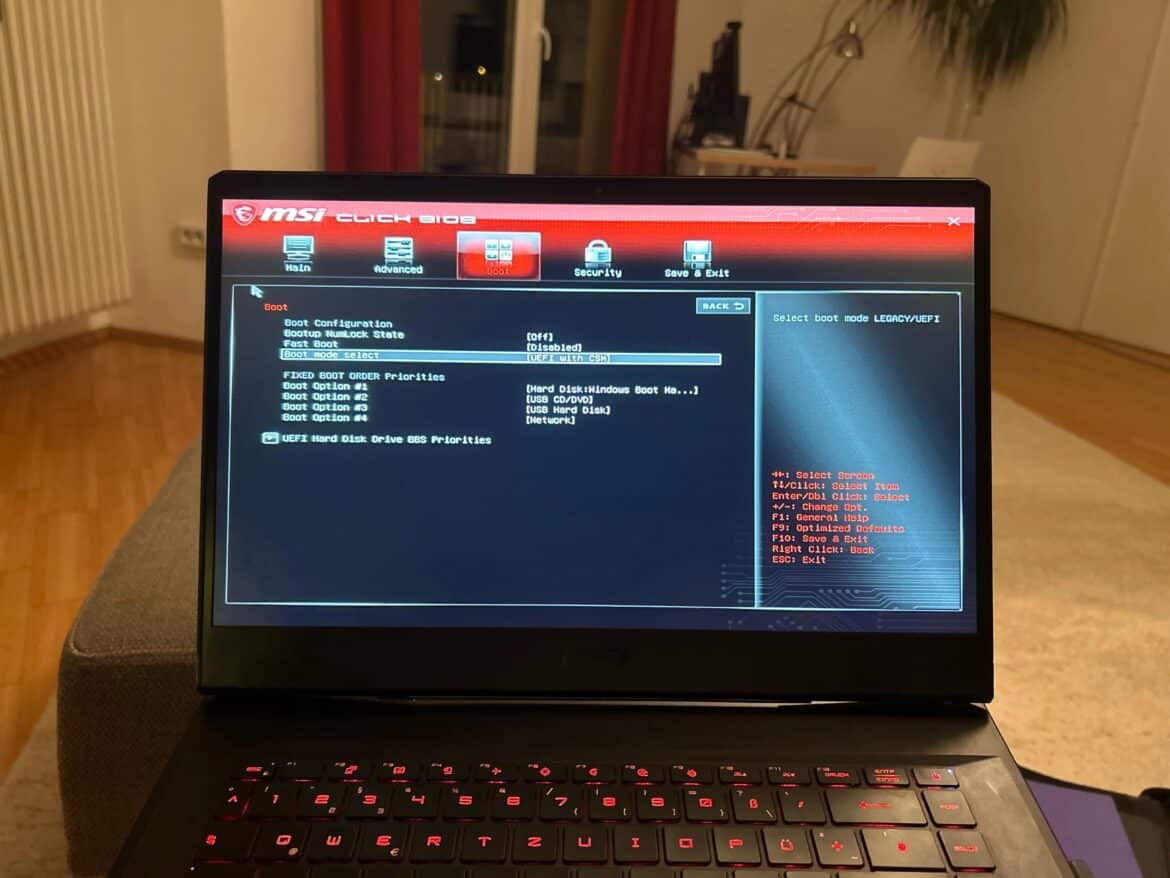
- Restart your PC and press the Delete key (on some models, this may be F2) several times during the boot process until the UEFI/BIOS menu appears.
- In the BIOS, navigate to the Boot tab and set the Boot Mode to UEFI if it is still set to Legacy/CSM.
- Disable the CSM (Compatibility Support Module) so that Secure Boot can be enabled.
- Ensure that Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 is enabled, as this is required by Windows 11 and Secure Boot.
- Go to either the Security or Boot tab.
- Find the Secure Boot option and set it to Enabled. On some models, you must first enroll the Secure Boot keys (“enroll factory default keys”) if the option is grayed out or a message such as “Repeat operation after enrolling PK” appears.
- Press F10, select “Save & Exit” and restart the PC.
- After a successful start, you can start msinfo32 in Windows and check whether “Secure Boot Status” is set to “On.”
- Common errors and solutions: Secure Boot cannot be activated – Check whether UEFI and TPM are active. You may need to rewrite the Secure Boot keys (PK) in the BIOS. Option not visible – Perform a BIOS update; older BIOS versions sometimes do not support Secure Boot. Error message during activation – Manually enter the platform key (PK) in the Secure Boot menu (“Enter all factory default keys”).
- These steps are valid for current MSI motherboards and BIOS versions. Pay attention to the model-specific menus and designations, which may differ slightly in some cases.
Advantages and disadvantages of MSI Secure Boot
Before you enable MSI Secure Boot, you should weigh up the advantages and potential disadvantages. The feature offers increased security, but can also lead to compatibility issues.
- A key advantage of Secure Boot is protection against malware that attempts to hide during the startup process.
- However, enabling it can lead to compatibility issues with older hardware or software that is not certified for Secure Boot.
- Another advantage is that it ensures that only trusted operating systems are started, which increases system integrity.
- A disadvantage is that additional steps are required to ensure compatibility when installing new hardware.
When you should disable MSI Secure Boot
MSI Secure Boot is not always suitable for all systems and users. There are scenarios in which disabling it may be useful, or alternative security measures may be necessary.
- If you are using an older operating system or special software that is not compatible with Secure Boot, you may want to disable the feature.
- Users of open-source operating systems may encounter problems, as not all of these systems support Secure Boot.
- In cases where specific hardware is not recognized, it may be necessary to disable Secure Boot to ensure full functionality.
- It is advisable to regularly review the need for Secure Boot and consider alternative security solutions if necessary.