2.3K
The “Extend Volume” issue prevents you from expanding storage space in Windows 10/11. In this article, you will learn why this option is sometimes unavailable and how you can resolve the issue step by step.
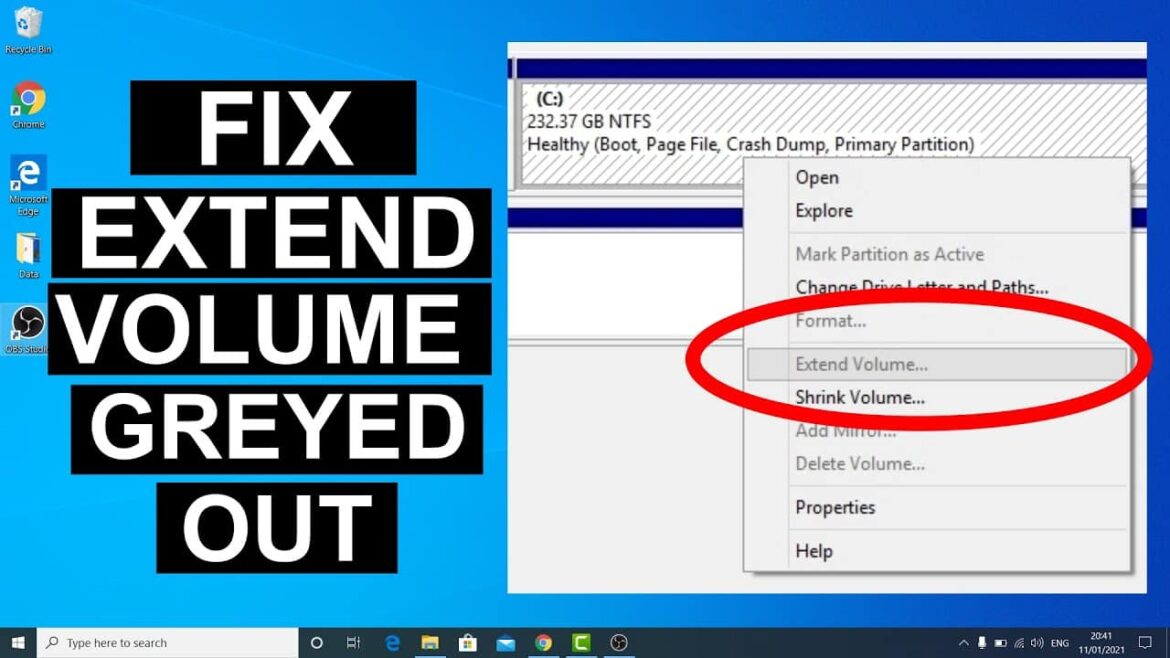
Extend Volume grayed out: Possible reasons
The “Extend Volume” option is sometimes not selectable in Windows Disk Management. This is usually due to certain technical requirements that are not met. The reasons for the “Extend Volume” option being grayed out are the same in Windows 10 and Windows 11.
- In most cases, the “Extend Volume” option is grayed out because there is no unallocated space directly behind the volume you want to extend. Windows requires that free space be immediately adjacent to the volume you want to enlarge. If the free space is further away or separated by other partitions, Disk Management cannot extend the volume.
- Another common reason is the file system of the volume to be extended. Windows Disk Management only supports extending NTFS partitions. If the volume is in FAT32 format, the option is grayed out – in this case, the file system must first be converted to NTFS.
- The partition style of the disk may also play a role. MBR (Master Boot Record) disks have a maximum partition size of 2 TB. If you try to extend a volume beyond this limit, the option will also be unavailable. These restrictions do not apply to GPT (GUID Partition Table) disks.
- Sometimes the volume to be extended is a system partition or is used by the operating system. In such cases, locks may occur that prevent the extension. Certain protection mechanisms such as system protection or running processes may also temporarily block the option.
Extend option grayed out: Possible solutions
Once you have identified the cause of the grayed out “Extend Volume” option, there are several possible solutions. Depending on the situation, you can use the following methods to fix the problem and make optimal use of your storage space.
- If the required free space is not located directly behind the desired volume, you must move it. Windows Disk Management does not offer a function for this, but you can use special third-party partitioning programs to move partitions and thus move the free space to the correct location. This will make the “Extend Volume” option available again.
- If the volume is in FAT32 format, you can convert it to NTFS using the “convert.exe” command. This can be done directly from the command prompt and does not require reformatting or data loss. After the conversion, the extend function will be available again.
- Sometimes it is necessary to delete or shrink adjacent partitions to create unallocated space. However, this can lead to data loss if you delete partitions. Therefore, be sure to back up all important data before changing or deleting partitions.
- Specialized tools such as AOMEI Partition Assistant or MiniTool Partition Wizard offer more flexibility than Windows Disk Management. With these programs, you can move, merge, or extend partitions without being bound by Windows restrictions. These tools are especially useful if you want to make more complex changes to your hard drive structure.
- In rare cases, system protection or missing permissions may prevent expansion. Check the settings under “System Properties” and make sure you are logged in as an administrator. If necessary, temporarily disable system protection to make the change.